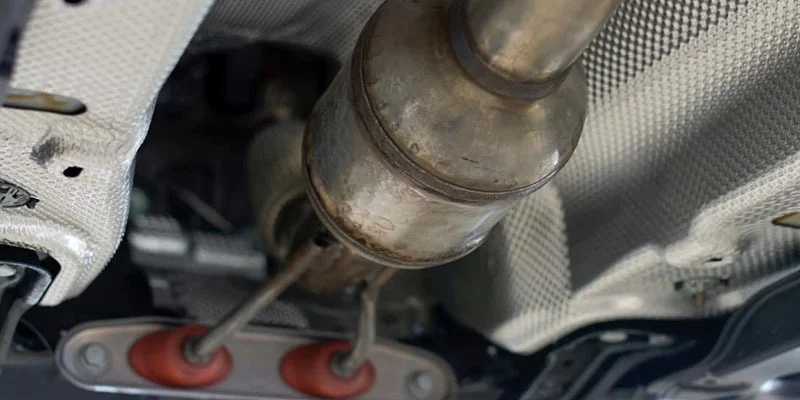
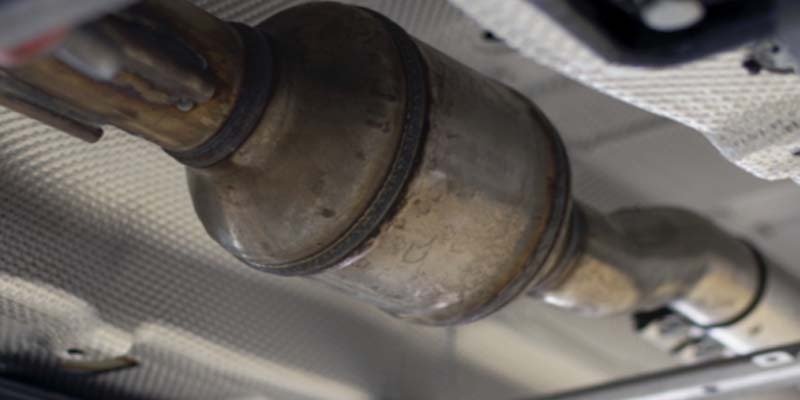
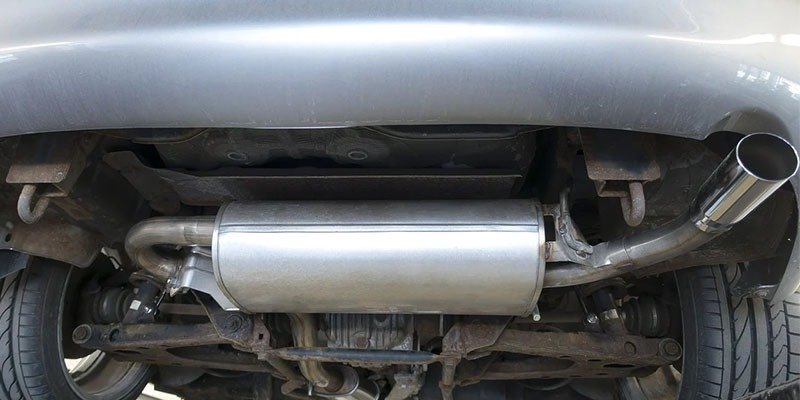
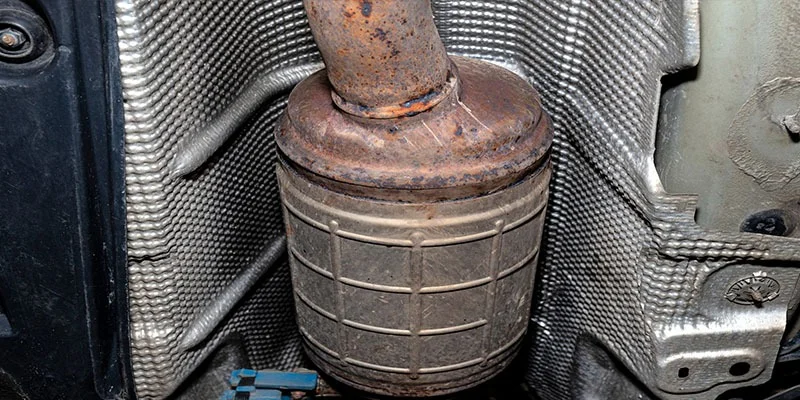
The catalytic converter is a device installed in vehicles to reduce harmful emissions from exhaust gases. This device converts toxic substances into less dangerous ones before they leave the car.
Catalytic converters are also known as three-way catalysts or TWCs. They are usually placed at the back of the engine compartment where the exhaust gas passes through them. These devices are designed to convert carbon monoxide (CO), unburned hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into harmless gases such as water vapour, carbon dioxide, and oxygen.
What Does a Catalytic Converter Make up of?
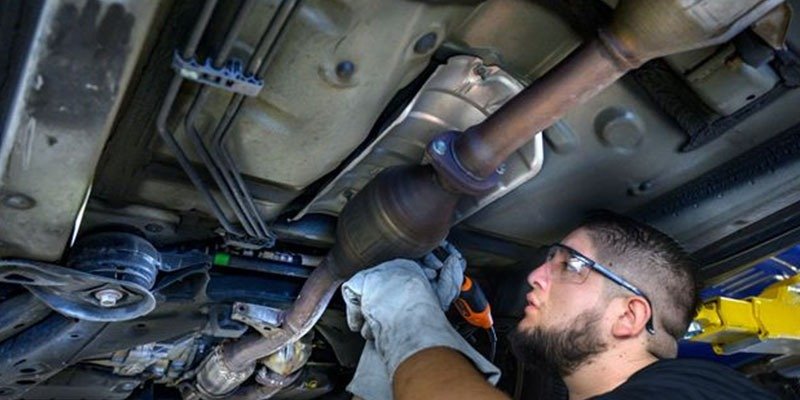

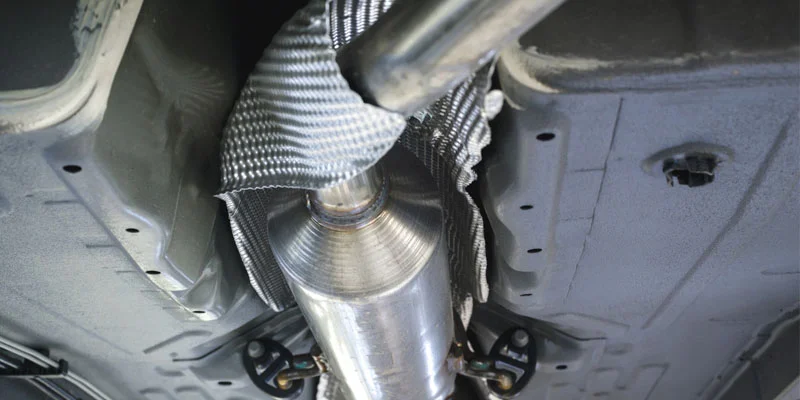
The catalytic converter consists of three main components: a catalyst material, a support structure, and a housing. The catalyst contains precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium. These metals are highly reactive and act like tiny magnets attracting the pollutants in the exhaust stream.
The support structure holds the catalyst material together while allowing the exhaust gasses to flow. The housing protects the catalyst material from damage caused by road debris and provides a place for the exhaust gasses to pass through.
History Of Catalytic Converter

Towards the end of the 19th century, the prototypes for Catalytic convertors were developed. Most of these prototypes were clay-based materials coated with palladium, platinum, and rhodium and then sealed with a double metallic cylinder.
The first production of the catalytic converter is credited to the series of Antonio Eleazar, Phillip Messina, Carl D. Keith, and John J. Mooney in 1973. They were first used in the United States Market after introducing strict emission standards.
How does a Catalytic Converter Work?
When an automobile engine runs, it produces heat and pressure that causes the fuel to burn. When this happens, the resulting combustion products include carbon monoxide, unburnt hydrocarbon, and nitrogen oxide. These chemicals react with the catalyst material inside the catalytic converter, converting them into harmless gases.
These gases are then released out of the tailpipe.
How does it work?
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up chemical reactions without itself being changed. It can be found in many things, including gasoline engines, diesel engines, and human bodies. In automobiles, the catalyst is called a catalytic converter.
In a catalytic converter, the catalyst helps break down harmful emissions like carbon monoxide, unburned hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides. Carbon monoxide is produced when burning fuels incompletely. Unburned hydrocarbons are created when the air/fuel mixture boils too rich. Nitrogen oxides are formed when there is excess oxygen present during combustion.
The catalyst works best if it has a lot of surface area exposed to the exhaust gas. The catalyst should be made of tiny particles with many contact points with the exhaust gas.
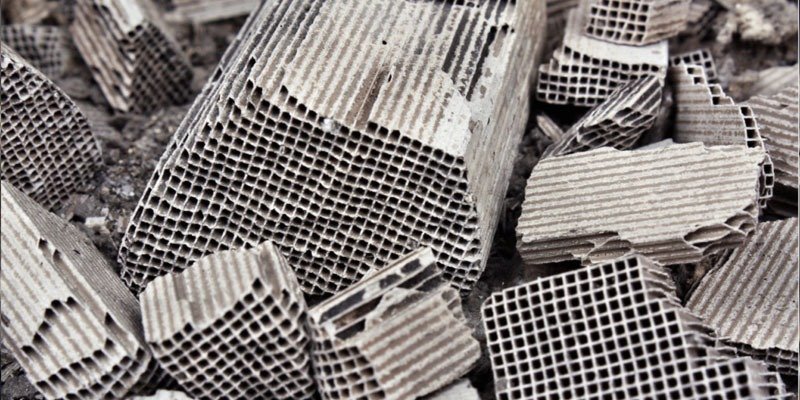
What is Inside a Catalytic converter?
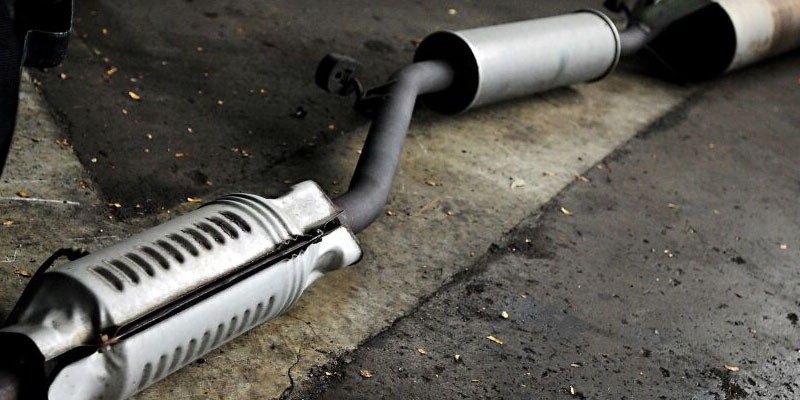

Any catalytic converter is typically made up of platinum or similar metal, such as palladium or similar metal. A ceramic honeycomb structure inside the cat housing is lined up with metals that help reduce emissions.
Here are the two main types of catalysts that are featured in most cars:
Oxidation Catalysts: Change the Carbon Monoxide into Carbon Dioxide by adding oxygen.
Reduction Catalysts: Removes the oxygen from nitrogen to reduce the nitrogen oxide emission and turn it harmless.
Generally, an Oxygen sensor is located near the catalytic converter to indicate the electronic control unit (ECU) about the level of oxygen found in the exhaust gas. It helps the vehicles to run on an efficient air/fuel ratio.
What are the Different types of Catalyst Converters?
Here are broadly Four types of Catalytic Converter:
1. Two-Way
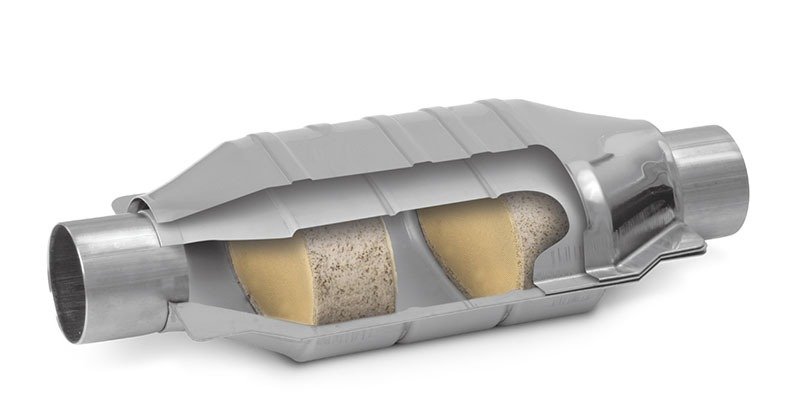
- A two-way catalytic converter comes with two simultaneous tasks:
- Oxidation of carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide.
- Oxidation of hydrocarbons to water and carbon dioxide
They were the ideal match for diesel engines that could reduce carbon monoxide and hydrocarbon emissions till 1981. But they were ineffective in controlling the nitrogen oxides, which gave way to the invention of Three-way converters.
1. Three-Way
After 1981, three-way catalyst converters were widely used in the vehicle emission control system in Canada and the United States. Here are the three simultaneous tasks of three-way catalyst converters:
- Conversion of nitrogen oxides to oxygen and nitrogen
- Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide to Carbon Dioxide
- Oxidation of Unburnt hydrocarbons to water and carbon dioxide
Once the catalytic converter receives the exhaust slightly above the stoichiometric point, the three-way converter works at their best
2. Diesel Oxidation Catalyst
Diesel Oxidation Catalyst is the most common catalytic converter in all diesel engines with compression engines. This catalyst uses O2 in the exhaust gas stream to convert the HC to H2O and CO2 and CO to CO2.
3. Lean Burn Spark-ignition Engines

The lean burn spark ignition process is similar to diesel engine catalysts as both emissions are highly similar.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do people steal the Catalyst Converters in Car?
Beaverton Police Department busted a Catalytic Converter theft racket of 14 people who stealth more than 3000 catalytic converters. In another case, the police arrested a group who have trafficked more than 44,000 stolen catalytic converters since January 2021. The estimated street value was over $22 million.
Catalytic converters are today worth more than gold. The combination of expensive materials such as Platinum, Rhodium, and Palladium is estimated to be thousands of dollars for every ounce. It is one of the prominent reasons why the Catalytic converter is the target of thieves. Hence, a typical Catalytic converter with an ideal combination of a few grams of these metals can easily fetch up to $1000.
Installing an anti-theft device by a repair shop is one of the effective ways to prevent catalytic converter theft. Always consider parking your car in well-lit areas to avoid theft.
Can I Drive Without a Catalytic Converter?
Yes! You can drive your car without any catalytic converter, but it may not pass the inspection. You need to install it in your vehicle to avoid any legal issues. If you don’t get it done, your vehicle will be considered non-compliant, and you will face fines.
Modern cars show an engine error code. As the converter is responsible for muffling the exhaust sound, you may notice an unusually louder noise coming from the exhaust.
It is possible to run the car safely without a catalytic converter.
What Type of Car has a Catalytic Converter?
All cars with combustion engines have catalytic converters in them. It is worth noting that Electric vehicles do not have catalytic converters because no combustion engine is involved.
How Much Does It Cost To Replace a Catalytic Converter?
Several factors influence the price of your catalytic converter. On average, you must spend $200 to $300 to replace a catalytic converter. Considering the newer vehicle fit, it requires a direct-fit converter which may go as high as $2500.
Which Cars Have Catalytic Converters?
Catalytic converters are an important part of modern vehicles with internal combustion engines. They are designed to reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful gases. Catalytic converters have been required on new cars since 1975, so any vehicle manufactured before then will not have one. Electric vehicles do not need a catalytic converter because they don’t have an exhaust system.
Conclusion
The purpose of a catalytic converter is to reduce the pollutants released from a car’s exhaust system. It uses a catalyst to convert toxic gases such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances like nitrogen and water vapour. It helps to improve air quality and reduce smog in cities and other populated areas. Catalytic converters are also beneficial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, which reduces global warming.

My Name is Christopher Angels, and I am a postgraduate in mechanical engineering. Cars have always excited me as a child, and soon I decided to dive into the world of cars by pursuing mechanical engineering. I also worked as a Mechanic for over 3 years to understand Cars’ anatomy and how each part contributes to its working.
My Name is Christopher Angels, and I am a postgraduate in mechanical engineering. Cars have always excited me as a child, and soon I decided to dive into the world of cars by pursuing mechanical engineering. I also worked as a Mechanic for over 3 years to understand Cars' anatomy and how each part contributes to its working.










