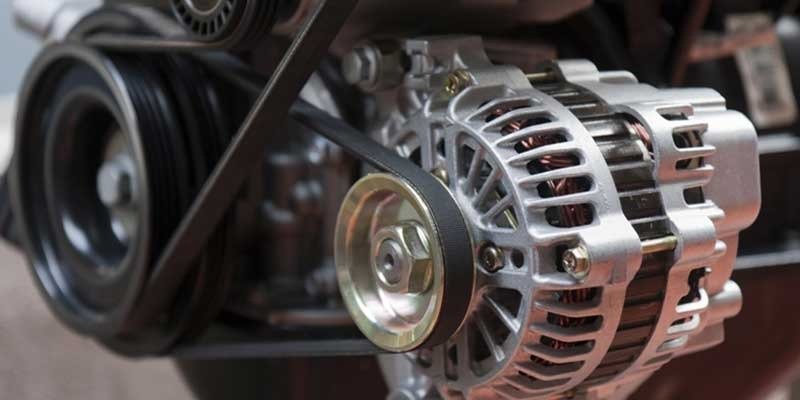
A car alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. This device helps recharge batteries and power accessories such as headlights and windshield wipers. What does it do exactly?
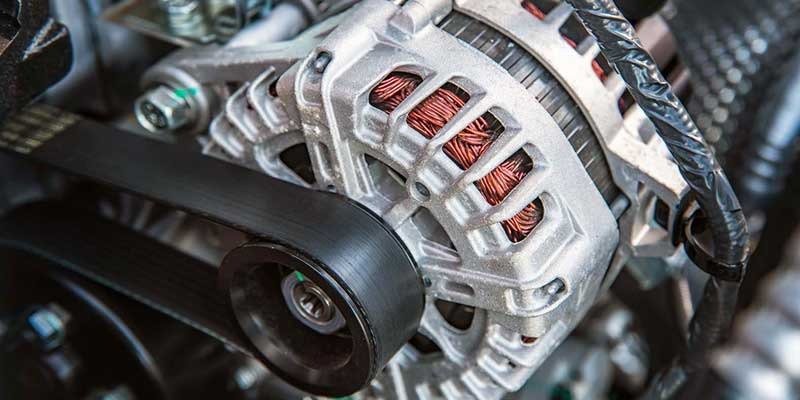
The alternator is a component of the vehicle battery system. It consists of two parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator generates alternating current (AC) electricity from the rotating magnetic field produced by the rotor. The rotor is attached to the crankshaft and rotates at high speed during operation. When the engine turns over, the rotor spins and creates a magnetic field. The stator coils pick up this magnetic field and convert it into AC electricity.
An alternator is a critical part of the vehicle’s charging system. Without it, the battery would only last a short time before completely draining.
How Does an Alternator Work?

In order for an alternator to work properly, there must be a connection between the rotor and the stator. The rotor has magnets that are connected to the shaft of the engine. The stator has copper wire wound around iron cores. As the rotor spins, the magnets pass through the stator winding creating an electric current.
Why Is an Alternator Important In A Car?
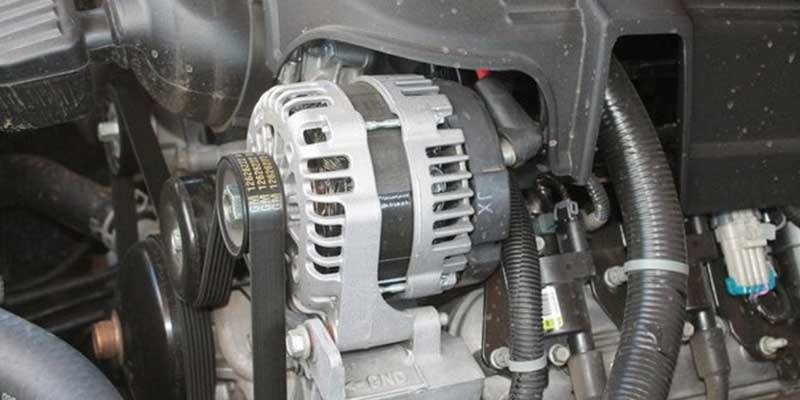

When you turn on your ignition key, the starter motor starts the engine. After the engine fires, the starter motor stops turning. At this point, the alternator begins generating electricity. If you have a dead battery, the alternator will keep the battery charged until the car can get to a service station or repair shop.
What Are Some Parts of An Alternator?
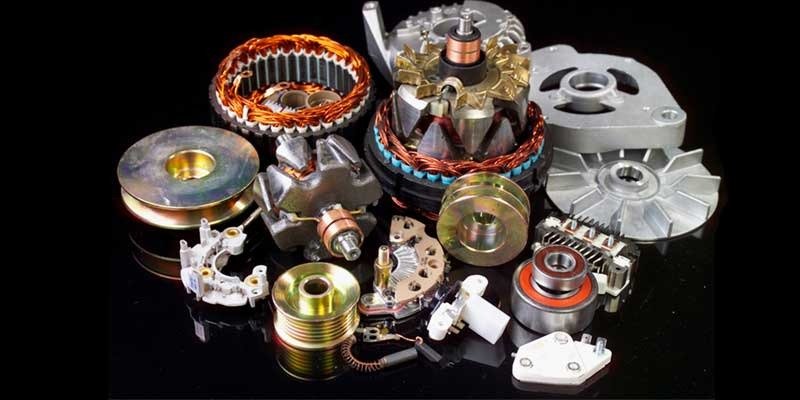

Stator – The stator is made up of many small wires wrapped around a core of iron. These wires create a magnetic field when they are energized with electricity.
Rotor – The rotor is the part of the alternator that actually produces the electricity. It contains a number of permanent magnets that rotate inside the stator.
A rotor is the part of an alternator that spins inside the stator. It’s the part that actually generates electricity. As the rotor rotates, it causes a series of alternating currents to flow through the stator windings. These alternating currents produce a magnetic field, which induces a current in the armature winding. This current produces direct current (DC), which powers the vehicle’s electrical system.
An alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. It does this by using a spinning rotor to generate a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the stator windings, inducing a current in the armatures. The current produced by the armature flows out of the alternator and provides power to the vehicle’s electrical system, including lights, radio, air conditioning and other devices.
Windings – The windings are the coils of insulated wire that make up the stator. They are usually wound around a steel core.
A winding is the length of wire used to connect the electromagnets to the battery. These wires are wound around the core of the iron inside the alternator. The number of coils determines the amperage output of the alternator.
Pulley – The pulley connects the alternator to the belt drive. It allows the alternator to spin freely without binding.
Voltage Regulator – The voltage regulator controls the output of the alternator. It regulates the amount of current flowing out of the alternator so that the correct voltage is delivered to the battery.
Belt Drive – The belt drive connects the alternator to other components of the vehicle’s electrical system.
Alternator Rectifier – An alternator rectifier is used to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). A typical alternator rectifier consists of six diodes. Each diode has two terminals, which means there are twelve total terminals on the rectifier. These terminals are called the anodes and cathodes.
A diode is a semiconductor device that allows electricity to pass in one direction only. When a diode is turned on, it allows electrical current to flow in one direction. When a diode turns off, it blocks any further current from flowing in that direction.
The function of an alternator rectifier is to rectify the alternating current produced by the alternator. The alternating current produced by the stator winding is converted to direct current using the alternator rectifier.
How Does Alternator Generate Electricity?
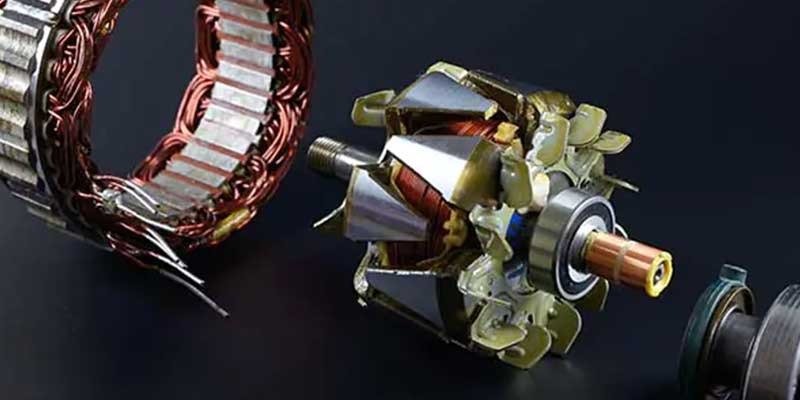

An alternator generates electricity by turning a crank shaft connected to the engine. As the engine turns, the crank shaft spins an alternator’s rotor. The rotor spins at high speeds, producing a magnetic field that moves past the stator winding. This causes electrons to flow through the windings, generating electricity.
How Long Does An alternator last?
An alternator is designed to last for the lifetime of your vehicle. However, this doesn’t happen every time. There are several factors that can cause your alternator not to work properly. These include:
- General Wear and tear
- Defective parts
- Corroded wires
- Use and exposure to water
- Heat damage
Your alternator may fail at any time. Even if it looks fine, there might still be problems inside. You should never assume that your alternator is working correctly. Always keep your eyes open for warning signs that your alternator needs service.
Conclusion
An alternator is a small yet indispensable part of your vehicle. It converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Without it, you would have no way to start your engine or charge your batteries.

My Name is Christopher Angels, and I am a postgraduate in mechanical engineering. Cars have always excited me as a child, and soon I decided to dive into the world of cars by pursuing mechanical engineering. I also worked as a Mechanic for over 3 years to understand Cars’ anatomy and how each part contributes to its working.
My Name is Christopher Angels, and I am a postgraduate in mechanical engineering. Cars have always excited me as a child, and soon I decided to dive into the world of cars by pursuing mechanical engineering. I also worked as a Mechanic for over 3 years to understand Cars' anatomy and how each part contributes to its working.